I. Core Positioning and Nomenclature
Positioning: Standard-type ball screw floating end (free end) support unit. Like BF, it is used at the non-drive end of the screw, allowing axial thermal expansion float and primarily withstanding radial loads.
Nomenclature Interpretation:
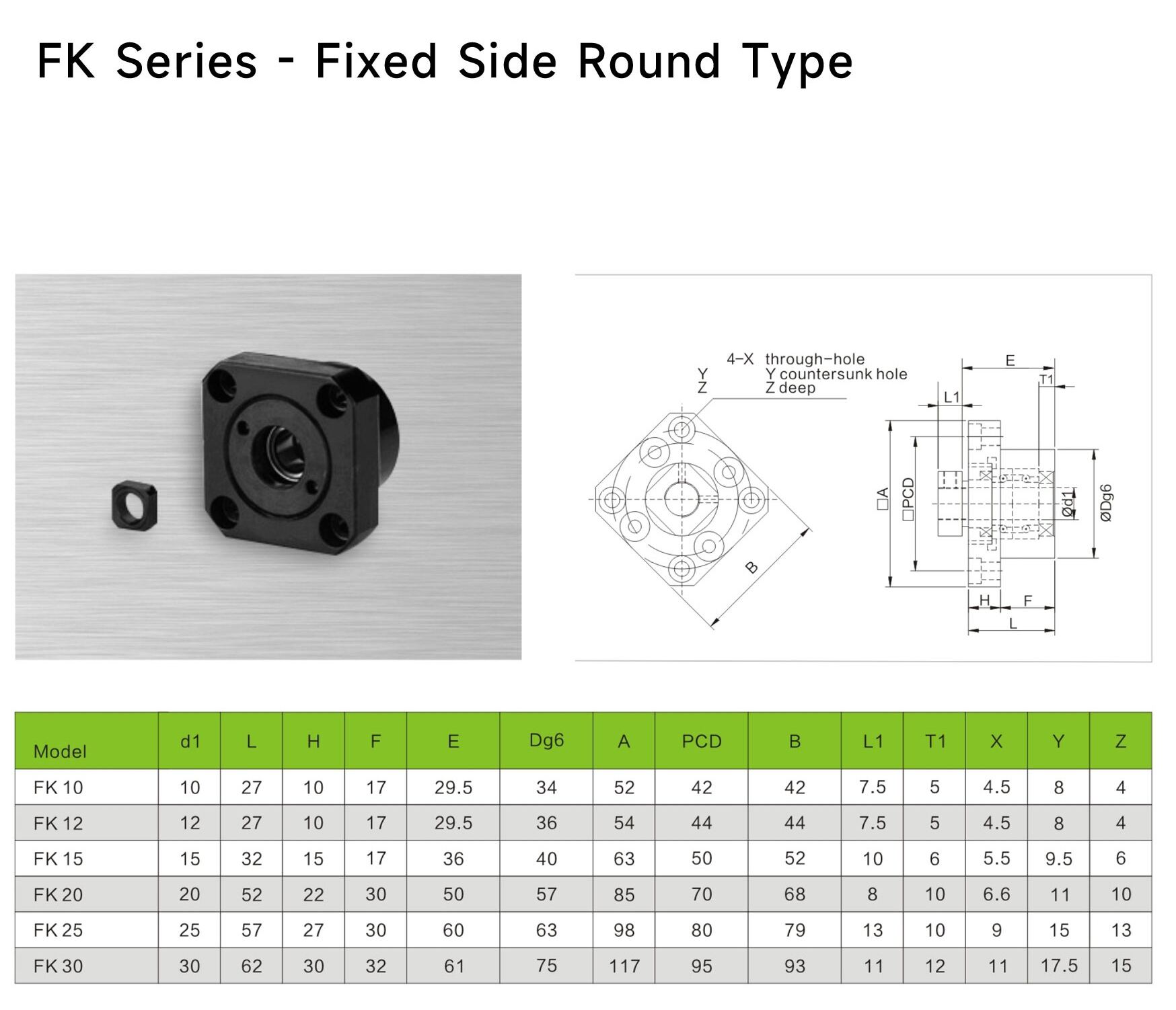
- F: Stands for "Flanged," referring to its square flanged housing structure, which is its most distinctive visual feature.
- K: Stands for "Simple Support" or originates from the German term for simple support. It is not related to "fixed" and in this context clearly indicates a floating end.
Core Value: Provides a structurally compact, installation-stable, economical, and reliable standard floating-end solution. It is the historically longest-standing and most classic pairing combination with the BK fixed end.
II. Core Structure and Design Features
The FK unit's design philosophy is simplicity, robustness, and practicality:
Square Flange Housing:
The housing is a monolithic square flange block, fixed via four mounting holes at the corners. This structure offers good torsional resistance and high mounting rigidity, making it the most common appearance in industrial equipment.
Internal Bearing and Floating Structure:
- Core Bearing: Typically uses a deep groove ball bearing, occasionally needle roller bearings. Its function is to provide excellent radial support.
- Floating Implementation:
- Method 1 (Common): The bearing outer ring is inside the square housing, axially located at one end by an end cover, with clearance left at the other end. When the screw expands thermally, the bearing outer ring slides axially within the housing.
- Method 2: The bearing inner ring has a clearance or light push fit with the screw shaft, while the inner ring is loosely axially limited by a snap ring or end cover (to prevent complete disengagement but not restrict thermal expansion sliding).
Sealing and Lubrication:
- Integrates standard contact seals for effective dust protection.
- Typically pre-filled with grease and equipped with a grease nipple for replenishment.
Connection to Screw Shaft:
The screw shaft end typically requires machining a snap ring groove for installing a retaining ring (snap ring). This ring's function is to prevent the bearing inner ring from accidentally sliding off the shaft end, but it does not restrict axial movement of the screw due to thermal expansion (the bearing inner ring can slide on the shaft). This is a key design commonality between FK and BF.
III. Core Features and Advantages
-
Robust Structure, Stable Installation:
The square flange design provides maximum resistance to overturning moments. Fastening with four screws offers good connection rigidity, making it highly suitable for industrial environments with certain radial forces and vibration.
-
Classic, Reliable, Economical, Practical:
As one of the most traditional floating-end designs, FK features mature structure, stable performance, well-controlled manufacturing costs, and excellent cost-effectiveness. It is the floating-end model with the largest market share and widest application.
-
Clear Pairing Relationship:
In most product catalogs, the BK fixed end and FK floating end are the default standard pair. They have corresponding sizes and coordinated designs, making them the "classic combination" preferred by engineers.
-
Pure Functionality:
Focuses on the core functions of the floating end—radial support and axial release—with an uncomplicated structure and low failure rate.
IV. Comparison and Selection Guide vs. BF and EF Floating Ends
| Feature |
FK (Square Flange Floating End) |
BF (Round Flange Floating End) |
EF (Eccentric Locking Floating End) |
| Housing Shape |
Square flange, strong torsional resistance, stable installation. |
Round flange, flexible installation, space-saving. |
Mostly round or square, but core feature is the eccentric locking sleeve. |
| Screw Shaft Requirement |
Requires a snap ring groove for installing a retaining ring to prevent detachment. |
Usually also requires a snap ring groove or small step. |
Plain shaft is sufficient, no machining required. |
| Locking Method |
Clearance fit + snap ring for anti-detachment. |
Similar to FK. |
Radial friction locking (eccentric sleeve). |
| Classic Pairing |
BK (square flange fixed end). |
Typically paired with the same series round flange fixed end. |
EK (eccentric locking fixed end). |
| Design Focus |
General industrial standard, robust and durable, good cost-effectiveness. |
Standard floating end in BF/BK systems, performance comparable to FK, different appearance. |
Optimized for plain shaft systems, emphasizes installation convenience. |
| Selection Logic |
Preferred when the fixed end uses BK and the screw shaft can be machined with a snap ring groove. |
Selected when the fixed end uses the same series round flange type. |
Mandatory when the fixed end uses EK and a plain shaft screw is used. |
Simple Selection Guide:
- Consider the Fixed End: The fixed end determines the floating end selection.
- Consider the Screw Shaft: Can/Willing to machine a snap ring groove?
- Can machine → If fixed end is BK, choose FK; if fixed end is a variant with a round flange BK, choose BF.
- Cannot machine (using plain shaft) → Fixed end must be EK, floating end must be EF.
V. Typical Application Fields
FK's application is as widespread as BK/BF, serving as the absolute mainstay in general industry:
- Non-drive ends of all types of CNC machine tools (machining centers, lathes, milling machines, etc.).
- Industrial robot joints and linear modules.
- Injection molding machines, die-casting machines, packaging machinery, printing machinery.
- Automated production lines, conveying equipment, material handling systems.
- Any general automation application using the classic BK-FK pairing.
VI. Selection and Usage Guidelines
- Paired Selection: Must select an FK unit of the same specification as the BK fixed end (e.g., BK12 paired with FK12).
- Screw Shaft Machining: It is essential to machine a snap ring groove meeting dimensional requirements at the corresponding position on the screw shaft and use a high-quality retaining ring.
- Correct Installation Direction: FK must be installed at the end of the screw furthest from the drive motor.
- Verify Floating Function: After installation, before finally tightening all mounting screws, gently attempt to axially tap the screw shaft end by hand or tool. A slight axial movement clearance should be felt, indicating normal floating function. Then fully tighten the mounting screws.
- Avoid Interference: Ensure there is sufficient space near the FK unit for the internal components to undergo slight axial sliding without any structural interference.
The FK support unit is the "classic" and "basic" model in the world of ball screw floating ends. It may not feature dazzling new technology, but its robust square flange structure, mature and reliable design, and excellent cost-effectiveness have ensured its enduring presence in the industrial field, making it the "gold standard" paired with the BK fixed end. Choosing FK means opting for a time-tested technical path with minimal risk and optimal cost, a fundamentally sound decision to ensure long-term stable operation of equipment.