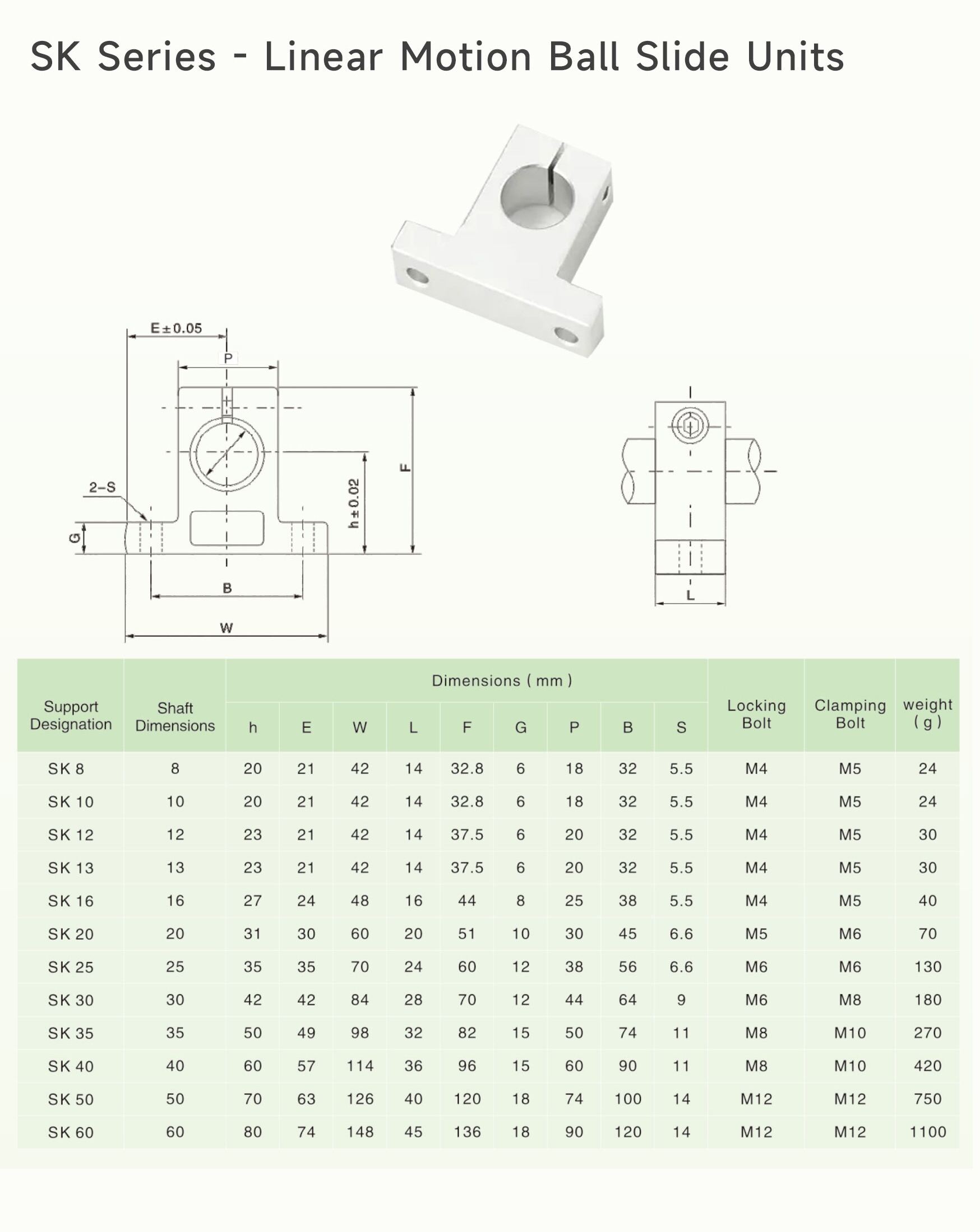
"SK" is also a standardized model of linear shaft support housing, widely used in the field of mechanical design. It typically refers specifically to the "Solid (Non-Split) Flanged Linear Bearing Housing," serving as either the classic "partner" or "alternative" to the SHF, depending on design requirements.
Positioning: Solid (one-piece) flanged linear bearing housing. Used for fixing and supporting linear shafts and their matching linear bearings.
Nomenclature Interpretation:
S: Represents "Support" or "Slide."
K: Possibly originates from the German word "Körper" (body/entity) or the Japanese concept of "fixation/kotei," emphasizing its integrated, solid, and fixed nature. This stands in contrast to the "split-type" and is its primary defining characteristic.
Most Critical Feature: "Solid / One-piece." The bearing housing is a single, indivisible component with a through bore.
Solid Structure (Key difference from SHF):
The housing is a single monolithic part. Its bearing mounting hole is a through, precision-machined circular bore.
Installation Method: The linear bearing and shaft must be assembled as a unit and axially inserted from one end of the housing until the bearing reaches its designated position.
Flanged Mounting Surface:
Typically a square flange with multiple mounting holes, providing a stable and rigid mounting foundation.
The bore size is precision-matched (typically a transition fit) to the outer diameter of standard linear bearings (e.g., LM, SC series).
Standard snap ring grooves are machined at both ends of the bore for installing retaining rings (circlips) to secure the linear bearing and prevent axial movement during operation.
Material and Finish:
Mostly carbon steel, with some aluminum alloy variants. Surfaces are often nickel-plated or black-oxidized for rust prevention and appearance.
Advantages:
Simpler Structure, Typically Lower Cost: The one-piece design reduces part count and machining steps, offering a cost advantage in mass production.
Higher Theoretical Rigidity: The absence of a split seam provides better structural integrity, potentially resulting in less deformation and more uniform stress distribution under load.
Stable Concentricity Post-Installation: The integral bore guarantees the housing's own coaxiality, unaffected by uneven screw clamping forces.
Slightly Better Dust Protection: The lack of a top cap seam reduces the path for dust ingress from above into the bearing area.
Limitations (Compared to SHF):
Inconvenient Assembly (Primary Drawback): Requires axial assembly. Assembly and disassembly become extremely difficult or even impossible in confined spaces, within pre-existing frames, or in densely packed multi-shaft arrangements.
Troublesome Maintenance: Replacing a bearing necessitates complete disassembly of the entire shaft and related components, leading to high maintenance workload.
Strict Installation Sequence Required: The shaft and SK housing must be installed very early in the overall equipment assembly process, limiting design flexibility.
| Feature | SK (Solid Flange Housing) | SHF (Split Flange Housing) |
| Core Structure | One-piece, non-separable. | Split-type, separable into upper cap and lower base. |
| Assembly Method | Axial insertion. Must be installed from the shaft end. | Radial clamping. Can be installed at any position. |
| Assembly Convenience | Poor. Severely constrained by space and assembly sequence. | Excellent. Allows flexible installation at any stage, ideal for confined spaces and later maintenance. |
| Rigidity | Theoretically slightly higher (no joint interface). | High, sufficient for the vast majority of applications. |
| Cost | Usually slightly lower (simpler structure). | Usually slightly higher (two additional parts and machined surfaces). |
| Maintainability | Poor. Replacing bearings requires extensive disassembly. | Excellent. Simply loosen screws to open the cap and replace bearings. |
| Applicable Scenarios | 1. Initial equipment assembly with unobstructed access. | 1. Space-constrained, structurally complex equipment. |
| 2. Cost-sensitive, high-volume production with ample assembly space. | 2. R&D equipment or experimental platforms requiring frequent debugging, maintenance, or upgrades. | |
| 3. Applications with special requirements for top-side dust protection. | 3. Precision multi-shaft workbenches. | |
| 4. Almost all modern, modular equipment designs. |
Selection Golden Rule:
Prioritize SHF: Unless facing irresistible cost pressure or specific design constraints, modern designs almost universally favor SHF. The value it provides in assembly and maintenance convenience far outweighs its minor cost increment.
Consider SK only in the following scenarios:
The equipment structure is extremely simple, with shaft ends completely exposed and clear axial assembly paths.
For mass-produced consumer-grade products where cost control per component is critical down to the cent.
As a low-cost alternative within a standard parts library.
SK support housings maintain their market share due to their cost advantage:
Simple-structure, mass-produced light-duty equipment: e.g., inside certain models of printers and scanners.
Low-cost DIY projects or educational models: Where assembly convenience is not a high priority.
Prototypes for initial functional verification: Built quickly without considering long-term maintenance.
Specific industrial equipment where its assembly limitations are fully understood and the assembly process is meticulously planned in advance.
Dimensional Chain Matching: Same as SHF. Select in this order: Shaft diameter → Linear Bearing model → SK housing bore size (e.g., φ8 shaft → LM8UU bearing → SK8 housing).
Strict Assembly Process Planning: Using SK housings requires detailed assembly sequence diagrams from the outset, ensuring sufficient space for axial insertion of the shaft and bearing.
Ensure Mounting Surface Accuracy: The mounting surfaces for multiple SK housings must be flat and parallel. Otherwise, inserting the shaft will be very difficult or may even jam. This often requires precision-machined mounting plates or fine adjustment with shims.
Always Use Snap Rings: After inserting the bearing, install snap rings at both ends. This is the sole safeguard against bearing axial creep.
Lubrication and Dust Protection: The SK housing itself has no seals. Ensure proper lubrication of the linear bearing and consider overall equipment dust protection measures.
The SK linear shaft support housing represents the "basic" and "economical" version of linear support components. It pursues ultimate structural simplicity and low cost as its core appeal but sacrifices the crucial benefits of assembly and maintenance convenience. In today's mechanical design trend emphasizing modularity, easy maintenance, and rapid iteration, the application space for SK is gradually being encroached upon by the more advanced SHF. Choosing SK signifies that the designer must make a very clear, and often difficult, trade-off between upfront manufacturing cost and the total lifecycle costs of assembly, maintenance, and flexibility. For most modern projects, SHF is usually the wiser and more future-proof choice.